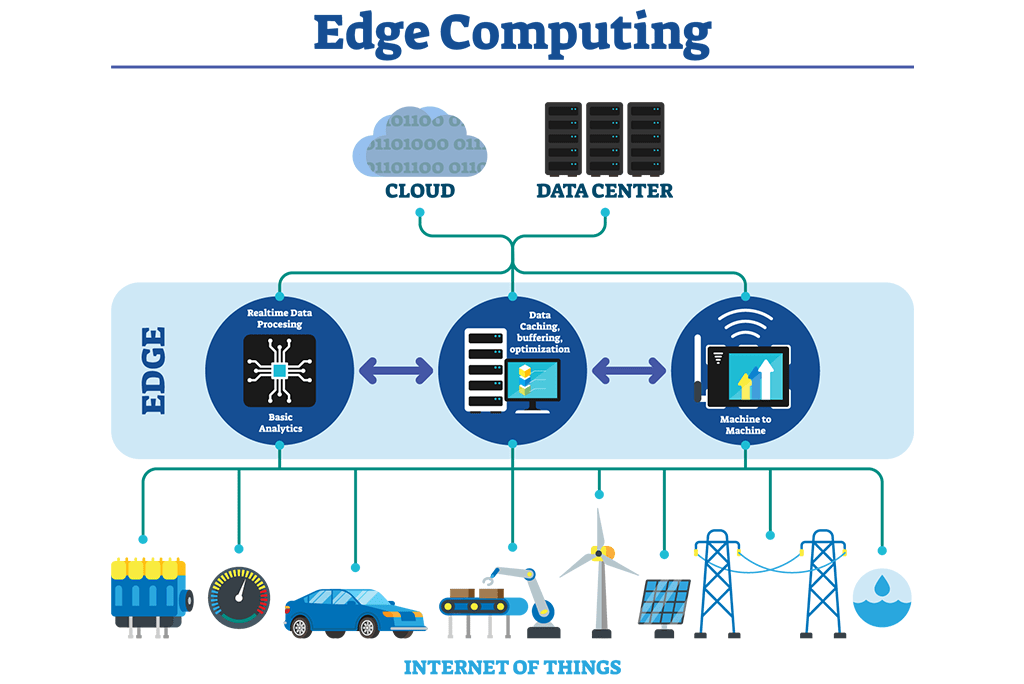
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, rather than relying on a centralized data-processing warehouse that may be located far away.
The “edge” refers to the devices or systems at the periphery of a network, closer to the source of data or where actions are required.
Empowering IoT:
1. Reduced Latency
Edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel between devices and the cloud. This is critical for IoT applications where low latency is essential, such as in autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare.
2. Bandwidth Efficiency
Edge computing can preprocess data locally, sending only relevant information to the cloud. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, saving bandwidth and making efficient use of resources.
3. Real-time Processing
Many IoT applications, like smart cities and smart grids, require real-time processing of data. Edge computing enables local processing and decision-making, allowing devices to respond rapidly to changing conditions.
4. Privacy and Security
By processing sensitive data locally, at the edge, organizations can enhance privacy and security. Critical data can be kept closer to its source, reducing the risk of exposure during transit to a centralized server.
Empowering Industry 4.0:
1. Real-time Monitoring and Control
Edge computing enables real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes. This is crucial in manufacturing environments where immediate responses to changing conditions can enhance efficiency and safety.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Edge devices can analyze data from sensors and machinery locally, predicting potential equipment failures. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing overall equipment effectiveness.
3. Decentralized Architecture
Industry 4.0 involves interconnected and intelligent systems. Edge computing supports a decentralized architecture where devices at the edge can communicate with each other, making the overall system more robust and resilient.
4. Scalability
Edge computing allows for scalable solutions, where additional edge devices can be added to the network without putting excessive strain on centralized resources. This is crucial in dynamic industrial environments with evolving requirements.
In summary, edge computing is a key enabler for IoT and Industry 4.0, providing the necessary infrastructure for low-latency, efficient, and secure processing of data at the edge of the network. This paradigm shift contributes to the advancement and optimization of various applications in these domains.
Enhancing Privacy and Security:
Edge computing plays a pivotal role in enhancing privacy and security across various domains, and its impact is particularly significant in the context of smart cities. Here’s how edge computing contributes to strengthening privacy and security in smart city environments:
1. Local Data Processing:
- Edge computing allows for the processing of sensitive data locally, reducing the need to transmit such data to centralized servers.
- This minimizes the risk of data breaches during transit, enhancing overall data security.
2. Reduced Exposure of Personal Information:
- By processing data at the edge, personal information of individuals residing in smart cities is less exposed to potential cyber threats.
- This aligns with privacy regulations and safeguards against unauthorized access to sensitive information.
3. Faster Incident Response:
- Edge devices can quickly analyze data and respond to security incidents in real-time.
- Rapid incident response is crucial for preventing security breaches and ensuring the safety of smart city residents.
4. Distributed Security Architecture:
- Edge computing enables a distributed security architecture, where security measures are implemented at the edge devices themselves.
- This decentralized approach enhances the overall resilience of the smart city’s security infrastructure.
Edge Computing in Smart Cities:
Smart cities leverage edge computing to optimize various aspects of urban living, from transportation to public safety. The integration of edge computing in smart cities brings about several benefits:
1. Real-time Decision Making:
- Edge devices process data locally, enabling real-time decision-making for critical applications such as traffic management and emergency response systems.
2. Efficient Resource Utilization:
- By processing and analyzing data at the edge, smart city infrastructure can make better use of available resources, leading to improved efficiency in services like waste management and energy distribution.
3. Enhanced Connectivity:
- Edge computing enhances connectivity by reducing latency, ensuring that devices in smart cities can communicate seamlessly and respond promptly to changing conditions.
4. Scalability and Flexibility:
- Smart cities are dynamic and ever-evolving. Edge computing provides the scalability and flexibility needed to adapt to new technologies and changing urban landscapes.
In conclusion, the integration of edge computing in smart cities not only optimizes operational efficiency but also addresses critical concerns related to privacy and security. The local processing of data at the edge enhances the overall resilience of smart city systems, making them more secure and privacy-compliant.
Top Edge Computing Trends in the Future
1. AI Integration at the Edge
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with edge computing is expected to be a significant trend. This involves deploying machine learning models directly on edge devices, enabling real-time decision-making and more efficient use of resources.
2. 5G and Edge Synergy
As 5G networks continue to roll out, there will be increased synergy between 5G technology and edge computing. The low latency and high bandwidth of 5G networks will enhance the capabilities of edge devices, enabling faster and more reliable data processing.
3. Edge-to-Cloud Orchestration
Future edge computing systems will likely involve seamless orchestration between edge devices and cloud resources. This ensures a cohesive and coordinated processing approach, optimizing workloads and enhancing overall system performance.
4. Edge Security Advancements
With the proliferation of edge devices, security becomes a paramount concern. Future trends in edge computing include the development of advanced security measures specifically designed for edge environments, addressing potential vulnerabilities and ensuring data integrity.
5. Decentralized Autonomous Edge Systems
The evolution of edge computing may lead to the development of decentralized autonomous systems, where edge devices can operate independently, communicate with each other, and collectively make decisions without relying heavily on centralized control.
Future Directions and Challenges:
While the future of edge computing holds promising trends, there are also notable challenges that need to be addressed:
Interoperability
Ensuring seamless communication and compatibility between diverse edge devices and systems remains a challenge. Standardization efforts will play a crucial role in overcoming interoperability issues.
Scalability
As the number of edge devices grows, scalability becomes a concern. Future edge computing solutions must be designed to scale efficiently, accommodating the increasing demands of diverse applications.
Data Privacy and Governance
The decentralized nature of edge computing raises concerns about data privacy and governance. Establishing robust frameworks and regulations to safeguard user data and ensure responsible data management is a critical future direction.
Edge Device Management
Managing a large number of edge devices distributed across various locations poses challenges in terms of maintenance, updates, and monitoring. Future developments should focus on effective edge device management solutions.
In conclusion, the future of edge computing holds exciting trends such as AI integration, 5G synergy, edge-to-cloud orchestration, security advancements, and decentralized autonomous systems. However, addressing challenges like interoperability, scalability, data privacy, and edge device management will be crucial for realizing the full potential of edge computing.